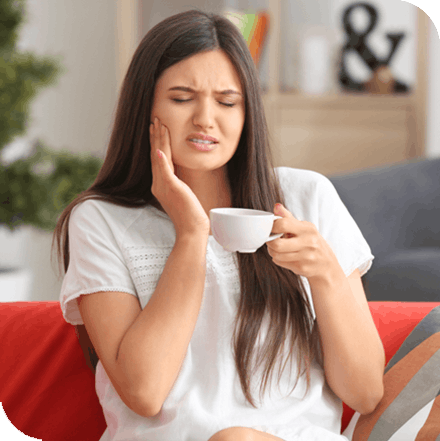
Does Mouthwash for Sensitive Teeth Work?

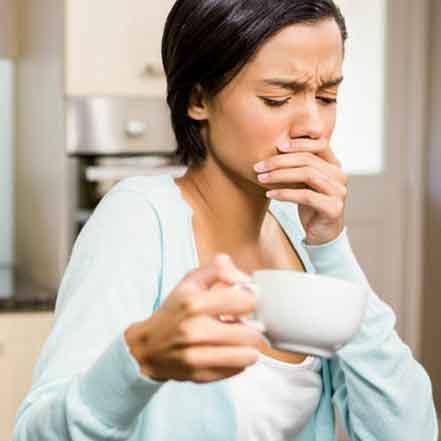
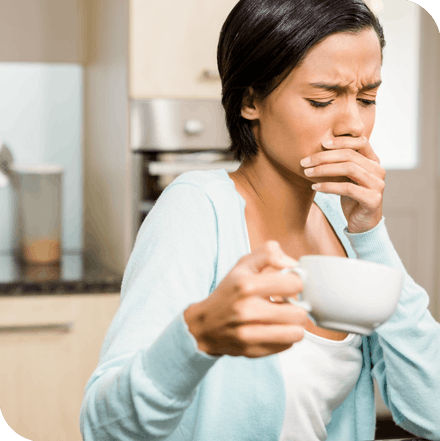
Have you ever noticed ice cold water or hot beverages like coffee and tea causing a short sharp pain?1 Does brushing or flossing your teeth make you grimace? If so, you may have sensitive teeth. Tooth sensitivity can be caused by several factors, some more serious than others, but luckily there are some solutions for relief. Alleviating discomfort from tooth sensitivity doesn’t need to be difficult or expensive—it can even be done from the comfort of your own home.
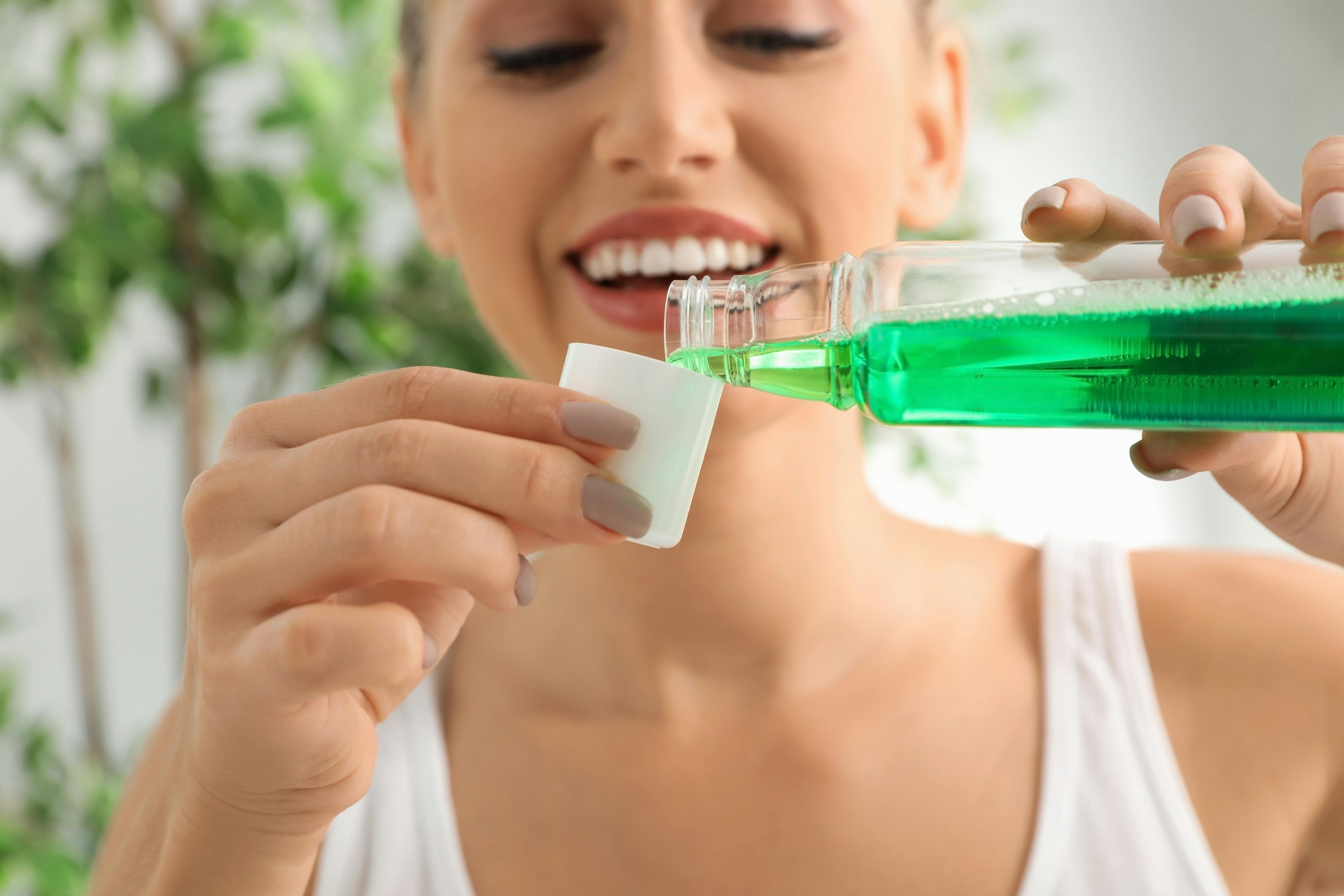
Depending on the cause of your tooth sensitivity, using certain dental products like mouthwash or toothpaste that are specifically made to treat sensitivity can help.1,2,5 Mouthwash for sensitive teeth and pain relief contains compounds to help calm the nerve or block sensations traveling from the surface of the tooth to the nerve.2 Although desensitizing dental products typically require several applications before sensitivity is reduced, it’s an easy and inexpensive way to treat sensitive teeth.
What Causes Sensitive Teeth?
If you experience uncomfortable, sensitive teeth, you might be concerned. Luckily, tooth sensitivity is not always a result of a serious dental problem.3 Tooth sensitivity can occur when the dentin, the underlying layer of your teeth, becomes exposed.6 Gum tissue covers and protects the tooth roots but receding gum tissue exposes the dentin. Tiny tubules in your dentin lead to the nerve center in your tooth, also known as the pulp. Exposed tubules allow for stimuli like hot or cold food to reach the nerve in your tooth, which can lead to tooth sensitivity or pain.6
Many different factors can lead to sensitive teeth, including:
- Age. Tooth sensitivity is typically highest between the ages of 20 and 40.3
- Acidic foods. Regularly eating or drinking acidic foods and beverages can erode your teeth’s enamel over time.3
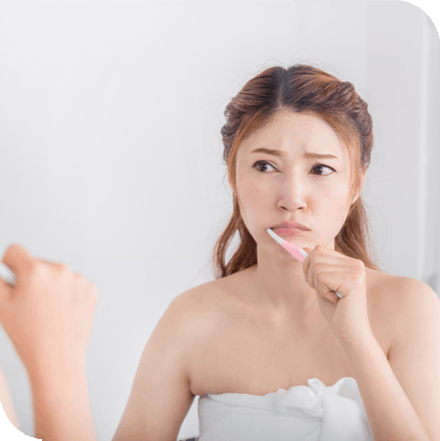
- Brushing too hard. Brushing too hard can wear down the enamel of your teeth, causing the dentin to become exposed.2,3
- Naturally receding gums. When gums recede away from your tooth, the root surface becomes exposed and can lead to tooth sensitivity.2,3
- Gum disease. A build-up of plaque or tartar can cause the gum to recede down the tooth. Exposed root surface leading directly to the nerve of the tooth can cause painful or uncomfortable sensitivity.2,3
- Teeth grinding. Also known as bruxism, grinding your teeth can wear down enamel and expose underlying dentin.3
- Cracked teeth. Broken or cracked teeth may cause sensitivity and discomfort.2,3
- Teeth whitening. Some patients may have tooth sensitivity for a short time during teeth bleaching or directly afterwards.3
How Does Mouthwash for Sensitive Teeth Work?
Desensitizing products, like toothpaste and mouthwash, work to reduce the nerve’s response to stimuli within the tooth’s pulp or by blocking the exposed dentin tubules.7 Depending on the ingredient used, desensitizing mouthwash may block sensation generated from your tooth’s nerve.7
Other Ways to Soothe Tooth Sensitivity
Desensitizing mouthwash can provide relief for sensitive teeth, but it’s not your only option.6 If you’re looking for a solution to your discomfort, check out these other ways to alleviate sensitivity:
Toothpaste
Desensitizing toothpaste can also provide relief for tooth sensitivity.2 When deciding whether to use toothpaste or mouthwash made for sensitive teeth, it’s important to remember you don’t have to choose just one. The desensitizing ingredients of these products are as effective in both forms.1,4,7
Desensitizing dental products contain different active ingredients that fight against sensitivity. When choosing a toothpaste for sensitive teeth, look out for some of these key ingredients:4
- Stannous fluoride
- Potassium nitrate
- Calcium sodium phosphosilicate
- Arginine
Good Oral Hygiene
Maintaining good oral hygiene can help prevent tooth sensitivity and protect your teeth.3 Properly brush your teeth twice a day, for two minutes a day, with a toothpaste containing fluoride.
Change Your Toothbrush
Using small, circular movements with a soft-to medium-bristled toothbrush can help prevent sensitive teeth.3 For best results, use the Sensodyne Sensitive Care Toothbrush with toothpaste for sensitive teeth.*
Avoid Certain Food and Drinks
If you have tooth sensitivity, drinking or eating something cold or very hot may trigger your sensitivity.3 Some people also have sensitivity when eating sweet or acidic food and drinks.3 Avoiding these foods and beverages when possible or using a straw may help your sensitivity.3
Professional Dental Care
If treatments for sensitive teeth don’t solve your discomfort, talk to your dentist. Teeth sensitivity may also be a cause of more serious dental problems. If you experience uncomfortable or painful sensitive teeth, contact your dentist. Some causes of sensitive teeth, such as tooth decay,2 require professional treatment. Even if your sensitive teeth don’t require more serious treatment like a root canal, professionals may suggest alternate treatments for sensitive teeth, like fluoride treatment to reduce the effects of sensitivity triggers to the nerve.6
*Sensodyne products are intended for relief of occasional dentin hypersensitivity that can occur when tooth enamel wears away and exposes the soft, inner part of your tooth called dentin. When the dentin is exposed and loses its protective covering, this can lead to hypersensitivity and discomfort when you eat hot foods, drink cold liquids, eat sweet or sour foods, or when you breathe through your mouth.
Source Citations :
- Dentine hypersensitivity. https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0020653920359566. Accessed 3/03/2022.
- Sensitive Teeth. http://www.ada.org/~/media/ADA/Science%20and%20Research/Files/patient_33.ashx. Accessed 7/13/21.
- Sensitive Teeth. Oral Health Foundation. https://www.dentalhealth.org/sensitive-teeth. Accessed 12/21/2021.
- Effect of desensitizing toothpastes on dentine hypersensitivity: A systematic review and meta-analysis. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/29787782/. Accessed 7/13/21.
- Mouthwash and a Toothpaste in the Treatment of Dentinal Hypersensitivity. http://www.medicinaoral.com/odo/volumenes/v4i1/jcedv4i1p28.pdf. Accessed 7/13/21.
- Sensitive Teeth. American Dental Association. https://www.mouthhealthy.org/en/az-topics/s/sensitive-teeth. Accessed 12/21/2021.
- Evaluation of the clinical efficacy of potassium nitrate desensitizing mouthwash and a toothpaste in the treatment of dentinal hypersensitivity. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3908806/. Accessed 3/3/22.