Can You Regrow Your Gums?
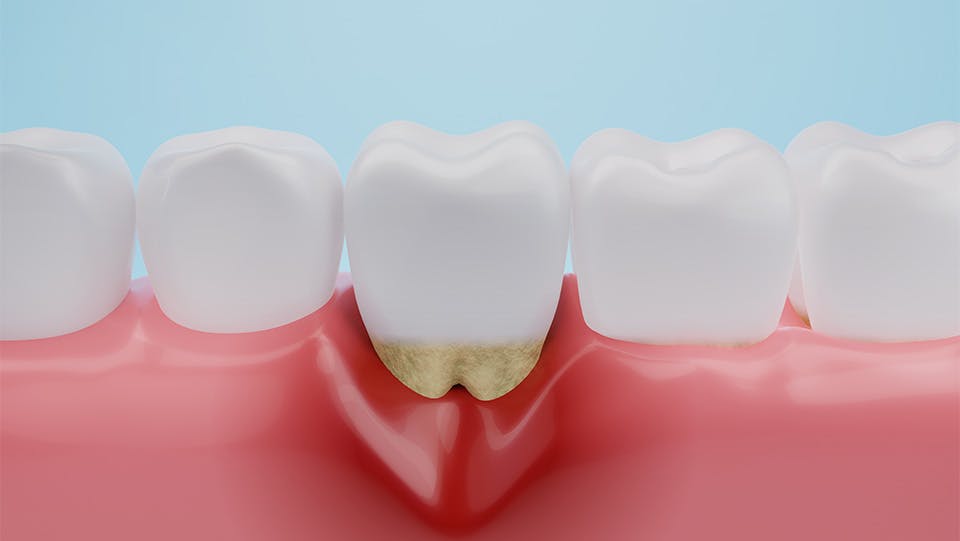
If you’ve noticed that your teeth look a little larger than they used to, your eyes may not be playing tricks on you. While your teeth haven’t changed size at all, your gums may be pulling away from your teeth, or receding, a common sign of gum disease.1 In fact, over 70% of adults older than 65 have gum disease which can include gum recession around at least one tooth.1 This isn’t limited to the older population, either, with younger people, ages 30 and up, experiencing similar conditions.1
If this is the case for you, you may be wondering how to restore your smile, and whether your gums will regrow on their own, or if you’ll have to resort to other treatment options. Learn what can cause receding gums and what can be done to treat this condition.
Will Your Gums Grow Back?
Your gums are a finite resource. Unfortunately, once they’ve pulled back from your teeth, they won’t regenerate or regrow on their own.1 While there has been some research into the matter, and some successful initial trials involving a thin membrane placed between the affected tooth or teeth and the gum, it’s still a long way off from being approved for the general public.2 While your gums will not regrow on their own, you may stop the problem from getting worse and avoid surgical options.
Why Do Your Gums Recede?
Taking care of your gums and maintaining good gum health is just as important as taking care of your teeth. Most people think of receding gums and immediately make the leap to gum disease but that isn’t always the case. There are several reasons as to why a person’s gums might pull away from their teeth:
- Crowded teeth. If your teeth were already crowded when your permanent teeth began to push through your gums, you simply might not have space for all of them and there might not be enough gum to cover the roots of your teeth.3
- Genetics. Some people are simply born with gums that are thin and fragile.1,3
- Aggressive toothbrushing. If your gums are thin and you’ve been using your toothbrush like a sandblaster, your gingival tissue may pull away.4
- Tobacco use. Whether you’re using chewing tobacco, cigars or cigarettes, tobacco products have a ton of negative health effects and one of them is recessed gums.1,4
- Gingivitis. This mild form of gum disease can cause your gums to become inflamed and bleed easily. While it is easily reversible, if left untreated, it may also cause your gums to pull away.5
- Periodontitis. If left untreated, gingivitis can worsen and stimulate an inflammatory response in the body that causes bones and tissues that support the teeth to become destroyed. If not addressed, periodontal disease can lead to tooth loss.1,5
- Age. As you age, your chances for developing gum and periodontal disease increases. Over 70% of Americans 65 and older have some form of gum disease.7
Treating Recessed Gums
Talk to your dentist about your concerns regarding your recessed gums. A dental professional can assess the cause and measure the amount of gum loss using a special tool called a periodontal probe.4
The treatment for recessed gums depends on the root cause of the condition. Your dentist may be able to camouflage any areas of recession with a tooth-colored dental filling or dental bonding that may make you feel more comfortable.4
But in most cases of severe gum recession, surgery is needed to correct the issue:1,4,6
- Periodontal Pocket Procedures. When your gums have pulled away from your teeth, there is a space, or “pocket” between the edge of your tooth and your gingival tissue, which can provide an area for bacteria to accumulate. Since your gums won’t regrow on their own to fill this space, your surgeon will remove affected tissue and smooth out the damaged bone to allow the gum tissue to reattach.
- Gum Grafts. This procedure helps to cover an exposed tooth root and prevent additional bone loss and gum recession. Your surgeon may take gum tissue from your palate on the roof of your mouth to cover the exposed area and may improve tooth sensitivity. There are several different types of gum grafting procedures and you and your surgeon can talk about the option that’s best for your situation.
Preventing Recessed Gums
Talk to your dentist about proper oral care. Consider how hard you’re brushing your teeth and opt for a soft-bristled toothbrush to avoid irritating your gums.4 Make sure you’re flossing to keep bacteria from building up between your teeth, and brush your teeth thoroughly twice a day.4
If sensitive teeth are an issue for you, due to gum recession or acid weakened enamel, reach for a toothpaste that addresses this specific concern like Sensodyne Sensitivity & Gum Whitening Toothpaste. If recessed gums are causing your teeth to feel sensitive, brush with a toothpaste that’s specially designed to help with gum problems.
Source Citations:
- How To Fix Receding Gums: 4 Top Options. University of Pennsylvania Penn Dental. https://mypenndentist.org/dental-tips/2023/05/17/what-to-use-for-receding-gums/. Accessed 6/2/23.
- Promising new treatment could regenerate gum tissue and prevent tooth loss. Oral Health Foundation. https://www.dentalhealth.org/news/promising-new-treatment-could-regenerate-gum-tissue-and-prevent-tooth-loss. Accessed 6/2/23.
- Gingival recession: Causes and treatment. Journal of the American Dental Association. https://jada.ada.org/article/S0002-8177(14)63227-X/fulltext. Accessed 6/2/23.
- Gum Recession. Cleveland Clinic. https://my.clevelandclinic.org/health/diseases/22753-gum-recession. Accessed 6/2/23.
- Gum Disease Information. American Academy of Periodontology. https://www.perio.org/for-patients/gum-disease-information/. Accessed 6/2/23.
- Surgical Procedures. American Academy of Periodontology. https://www.perio.org/for-patients/periodontal-treatments-and-procedures/surgical-procedures/. Accessed 6/2/23.
- Gum Disease Risk Factors. American Academy of Periodontology. https://www.perio.org/for-patients/gum-disease-information/gum-disease-risk-factors/. Accessed 8/29/2023.